Performance Characterization of Microsoft SQL Server on VMware vSphere 6
Executive Summary
Large Microsoft SQL Server® databases can achieve great performance and fully utilize current-generation server and storage technology using VMware vSphere®. With the introduction of vSphere 6, larger physical hosts are supported more than ever before (up to 480 processors and 12 TB). In this paper, a variety of vCPU and virtual machine combinations were tested on current-generation hardware to show that vSphere 6 can handle hundreds of thousands of online transaction processing (OLTP) database operations per minute.
Introduction
VMware vSphere provides an ideal platform on which customers can virtualize their business-critical applications, including databases, ERP systems, email servers, and emerging technologies such as Hadoop. A full discussion of the benefits is included in the whitepaper “Virtualizing Business-Critical Applications on vSphere [1]”.
A business-critical application that is often run on vSphere is Microsoft SQL Server, which is “one of the most widely deployed database platforms in the world, with many organizations having dozens or even hundreds of instances deployed in their environments [1].” Consolidating these deployments onto modern multi-socket, multicore, multi-threaded server hardware is an effective solution for administrators and their organizations.
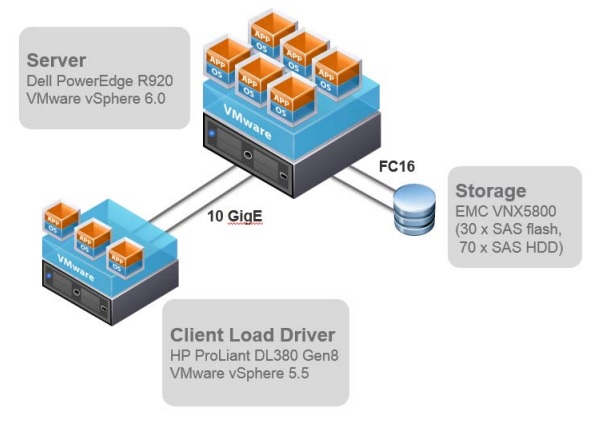
Achieving optimal SQL Server performance on vSphere has been a focus for VMware. Last year a series of performance tests with SQL Server on vSphere 5.5 [2] using a four-socket Intel Xeon E7-4800 based server was published. That whitepaper showed excellent performance up to the maximum size virtual machine supported at the time. This new study sizes the VMs similarly and uses the same methodology, but with vSphere 6 and Intel Xeon E7-4800 v2 based processors (codenamed “Ivy Bridge EX”). With vSphere 6, VMware supports much larger “monster” virtual machines that can scale up to 128 virtual CPUs and 4 TB of RAM [3]; however, scaling to these new limits was not possible with the hardware used in this study. There is another study published recently using vSphere 6 and Oracle 12c [4] that scales a database workload from 15 vCPUs to 120 vCPUs.
The new tests show large SQL Server database instances continue to run extremely efficiently, achieving great performance in a variety of virtual machine configurations on vSphere 6. Only minor tunings to the SQL Server application and the vSphere 6 ESXi hypervisor were needed to fully optimize these large virtual machines.
Additionally, this new study includes several tests with CPU affinity to show the performance differences between physical cores and logical processors (Hyper-Threads), the maximum throughput achieved using multiple virtual machines that vary in virtual CPU and memory sizes, and experiments with the advanced Latency Sensitivity setting offered by vSphere.
Download :
Performance Characterization of Microsoft SQL Server on VMware vSphere 6.pdf